Pepper Blight is caused by the pepper phytophthora capsiciL.) destruction of soil borne diseases [1]. Since 1918 in New Mexico, the United States first discovered blight in Pepper harm since, disease has in the main pepper producing areas of the world generally occur, become the main diseases of pepper production. Most scholars believe that pepper to Phytophthora capsici no immunity, part of the material of epidemic disease has some resistance, but inheritance of resistance is quite complex, mainly including three single gene genetic, oligogenic inheritance and multi gene genetic point of view, the majority of scholars tend to pepper to Phytophthora capsici resistance is controlled by polygene quantitative traits of [2].
In 1984, the first genetic linkage map was constructed by using the F2 mapping population obtained from the hybrid of annual Pepper Cultivar and Chinese Pepper Cultivar Tanksley[3], thus creating the first of the establishment of the genetic map of pepper. In 2012, Mimura and [4] were the first time to establish 12 linkage maps by SSR molecular markers, which were consistent with the number of hybrid chromosome in the annual pepper culture, breaking the breaking of the previous linkage map. Thabuis 5 by 3 pepper species between molecular genetic map of QTL analysis to six and anti disease related to the main effect QTLs.Quirin etc. [6] study found that blight resistance QTLs Phyto. 5. 2 in many anti source materials are present.
[7] et al. Lefebvre et al. Studies have found that 13 Pepper Blight Resistance is related to QTLs, and the different QTL have different contribution to the phenotype. Use Parker Joe e * cm Ogundi-win [J] 334 construction of F2 population found five and anti disease gene related QTLs: Phyto-Q, Phyto-R, Phyto-S, Phyto-T and Phyto-U can explain phenotypic variation rate of 89. 6%. Chen Xiaoying [9] to B072 and 13088 in two pepper resistant and susceptible susceptible inbred Hybrid F2 population as materials, screening to 2 and resistance gene linked SSR markers and they initially located in pepper of the five linkage groups. But because different researchers use the Anti Sense material and the strain of the fungus is not exactly the same, so that these QTL sites can not get mutual evidence.
This study use high international recognized Pepper Blight material PI201234 and breeding of highly susceptible disease materials g29 as test materials construct F2 population and analysis of resistant gene to Phytophthora capsici and QTLs, trying to discover new resistance genes, lay a foundation to further development and spicy pepper blight resistance gene closely linked molecular markers, speeding up China's pepper phytophthora blight resistance breeding process.
1 materials and methods.
1.1 test material.
PI201234 for the Jiangsu Provincial Academy of Agricultural Sciences vegetable pepper research group from the Asian Vegetable Research and development center of the international recognition of the international recognition of pepper. G29 is the high generation inbred lines of sweet pepper materials in Jiangsu Province Agricultural Sciences vegetables pepper research group of independent selection, high sense of disease. 2012 5 August in Jiangsu Province Academy of Agricultural Sciences vegetable experimental base plastic greenhouse to PI201234 as female parent, g29 as male parent, artificial emasculation hybridization, F12012 years 9 to 12 month F1 plant self stud obtain F2. Used in the test of Phytophthora capsici provided by Jiangsu Province Academy of Agricultural Sciences of agricultural resources and environment research Institute, the pathogens collected from Huaian City, Jiangsu Province, belonging to race 1 of small (Ph1).
1.2 test methods.
2.1 1 pepper F2 groups to identify the resistance of the disease to take F2 generation seeds in the nursery seedlings to grow seedlings, to grow after four true leaves, respectively, into the diameter of 10 cm nutrition bowl, plant breeding and do the next label. Method of reference Lin Baiqing etc. [11] for the cultivation of Phytophthora capsici zoospores: first remove the paraffin oil in the preservation of hyphae in potato culture medium activation, 28 degrees darkness culture after 5 days, cut 1 cm3 of potato based switching culture in medium with V8, light (4 000 LX, 12h) training 10 days induced sporangia. Before inoculation, 10 ml sterile water was injected into the culture dish of the V8 medium, and 30 min was placed at 4 ~60, and 30 min was placed at room temperature (20 degrees C) to induce the release of the spores. Scrub with sterile brush, 4 layers of gauze filtration, obtain zoospore suspension. The number of blood count for the spores of zoospores of mother liquor. The inoculation method was used in this experiment, the inoculation method was used to inoculated [12]. in the F2 population seedling 6 ~8 leaf inoculation, 1 d before inoculation.
Will zoospore mother liquid diluted into spore concentration was 1 ml 1 x 104 of the solution, the amount of cylinder from 20 ml evenly poured around the plant, plastic film moisturizing 24 hours. Transfer to the artificial climate box, at a temperature of 28 degrees, 90% relative humidity, illuminance 4 000 LX, 12 h / D under the condition of culture prompted morbidity. After inoculation with 15 d, according to the Ministry of agriculture in 1999 promulgated the classification criteria for the investigation of the level of incidence (Table 1).
1. 2. 2 DNA extraction and molecular marker analysis DNA extraction: when the seedlings grow to clover heart, take the start of the young leaves, DNA was extracted by improved CTAB method [13] by UV spectrophotometer to determine the concentration of DNA. SSR molecular marker analysis: 664 SSR markers used in the mapping, which according to the EST sequence design mark 540 to, 45 of the labeled reference Ince, [14] published SSR markers, 79 pairs of primers from http: / primer /solgenomics. net/. were by the Shanghai SANGON biological have limited synthesis. PCR system for 20. 0 g l, system containing 2 fold enrichment PCR amplification of pre mixed solution 10. 0 g l (including Mg2 + 10 x PCR buffer, 2. 5 mmol / L dNTPs, 0. 5 u Taq DNA polymerase, DNA 50 ng, upstream and downstream primers for 0. 3 mol / L and ddH2O 6. 0 g l, instant centrifugal mix, was amplified by PCR reaction. Amplification procedures: 94 C pre denaturation of 4 min; 94 degrees of denaturation 30s, 55 C annealing 30 s, 72 C extension of 50 s, 30 cycles; the last 72 degrees to extend 7 min, 4 degrees to save the PCR product. PCR product was detected by 10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and silver staining.
1. 2. 3 genetic linkage map construction and QTL analysis and separation of offspring and female parent with the same type with a said, with the male with the same type of use B said, two parents heterozygous bands represented by H. Join-Map 4. 0 software. Using LOD value (logarithm of odds) is more than or equal to 2 as the threshold using the Kosambi mapping function, construction of molecular linkage map. The choice of multi model QTL mapping method (multiple QTL model, the MQM) detection may exist the MapQTL4. 0 software QTL[15]. when the LOD value greater than or equal to 2, indicating that possible linkage between two pairs of genes. The genetic effects of each QTL and the contribution rate of phenotypic variation of this trait were calculated.
2 knot fruit.
2.1 pepper F2 groups to identify the results of the disease.
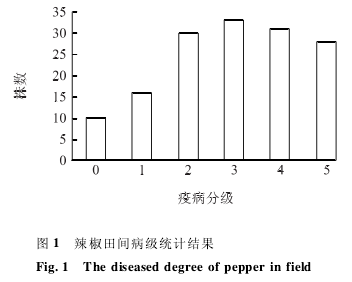
Phytophthora capsici inoculation in 6 to 8 leaf stage in F2 population a total of 148 per plant, after 25 DEG C cultured for 15 days, according to disease classification statistics and pepper disease grade feeling sick trees into approximation is normal distribution (Figure 1), which can be speculated that, the resistance to Phytophthora capsici material PI201234 is a quantitative trait controlled by multiple genes.

In the course of the investigation found that some plant disease faster, inoculation after 5 d, lower leaves appeared yellow symptoms or even fall off; and some plant disease relatively late, early asymptomatic or not obvious, finally have mild symptoms, to Phytophthora capsici showed certain resistance. From the whole point of view, the disease is gradually increased with the cultivation time. Statistical results show that zoospores irrigation root inoculation incidence with the past in field production of natural disease incidence results consistent, basically can be simulated field disease, applicable to the identification of pepper phytophthora blight.
2.2 construction of genetic linkage map.
Using 664 pairs of SSR primers to amplify the parental lines, a total of 141 pairs of polymorphic primers were obtained. Due to the subsequent anti disease related QTL mapping, it is necessary to use the method of composite interval mapping, therefore, to exclude amplified polymorphic band might belong to the dominant gene primers, namely those in the parents can be amplified bands, and the zone size is not the same primer selection. In addition, taking into account the definition, brightness and stability of polymorphic bands, 65 pairs of SSR primers were selected to analyze the genotype of F2 population. The amplified polymorphic bands were mostly concentrated in the 100 bp ~250 (Fig. 2).
Using JoinMap 4 mapping, we found that 65 SSR markers were distributed on 10 linkage groups (N1 ~ N10). The number of markers on each linkage group was 2 ~12, and the number of markers on each linkage group was 6.5. The length of single linkage group was 2.1 ~95. 7 cM, the total length was 418.6 cM, the average genetic distance between the two markers was 6 44cM (Fig. 3).
2.3 QTL analysis of resistance to blight.
Using mapqtl 4.0, using composite interval analysis method, a cofactor for EST451, EST191, EST442 and EST473. in N3 linkage groups obtained a correlation with disease resistance QTL, located in the EST451 ~EST191 can explain the resistance to Phytophthora Blight in phenotypic variation of 14. 9%.
3 discussion.
3.1 methods for the identification of resistance to blight.
Against Phytophthora capsici in Pepper identification of common method with zoospores irrigation root, stem cutting inoculation, from the systemic collateral inoculation method, spray inoculation method [16], each method have their respective advantages. In view of P. capsici is of sporangia germination produce motile spores infect root cause disease. Therefore, this experiment used zoospore pouring the root of pepper to Phytophthora resistance biology identification. The results show that zoospores root irrigation method can be effectively divided into pepper F2 population among the single strains of resistance, plant to reflect the true resistance. Ituyo [17] compare the zoospore irrigation root, stem cutting inoculation and from leaf inoculation method of inoculation effect, also think that irrigation root inoculation method may be closer to Phytophthora Blight of pepper processes occurring in the field, most can reflect the variety of true resistance. [18] was considered to be a simple method of stem cutting, and it was not necessary to culture mycelium and spore capsule, and to quantify the disease resistance when compared with the inoculation method. But in the process of inoculation, the concentration of the pathogen, the growth period of pepper, the temperature and the humidity of the environment will have a great influence on the inoculation effect. Therefore, the identification of disease resistance should be strictly controlled inoculation conditions, to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the identification results.
3.2 Pepper Resistance inheritance.
In this study, the use of pepper resistance material is PI201234, by Phytophthora species of small Ph1 after inoculation, at all levels of diseased plants was approximately normal distribution, in line with the model of quantitative character inheritance. Therefore it is suggested that the inheritance of resistance to Phytophthora capsici Ph1 PI201234 belong to multiple genes control the number of genetic. Jiang Lanjun [J] also in this regard for the study and that the resistance to Phytophthora capsici PH3 in PI201234 with 1 pair incomplete dominant gene genetic model, and genetic of Ph1 resistance is not consistent with this model, and the results are similar. While Kim and other [20] studies were contrary to this study, he believed that the resistance of PI201234 was controlled by 1 incomplete dominant genes. Resistance genetic mechanism of a chili PI201234, results of different scholars have different, in addition to Phytophthora capsici physiological of different, may also and they use sense disease material about different, plus on Phytophthora capsici is easy to produce the new race, the PI201234 genetic mechanism study of more diverse, this situation also appeared in other peppers resistant materials research. So on the pepper resistance to disease resistance breeding, should be based on the accurate genetic analysis of materials and resistance, to determine the breeding line of resistance to blight.
Genetic linkage map and QTL analysis of 3.3 pepper.
Since the advent of the world's first pepper genetic map, scientists at home and abroad have set up more than a dozen maps, the number of chain groups to build is not the same. The test and Zhang Baohan in 10 linkage groups of genetic map was constructed with a high resistance to disease material PI201234 and high sense of epidemic materials g29 and pepper 12 chromosomes, resulting in the number of linkage groups is less than the number of chromosomes in the reason may because using EST-SSR markers. EST-SSR molecular marker has the advantages of simple operation, strong stability, compared with SSR markers, more conducive to the research work of linked genes, but due to the source of EST-SSR primer design for the expression of a gene, resources are not rich enough to covered the entire genome, pepper.
The genetic linkage map constructed by Minamiyama and [21], including 15 linkage groups, more than the number of chromosomes, the analysis may be due to the smaller density of markers, resulting in a broken chain group. Until 2012 Mimura and other [22] was the first time using SSR molecular markers to establish a 12 linkage map group, breaking the previous break of the chain map.
QTL localization on Pepper Resistance to disease, previous work done a lot of research work. Minamiyama etc. [21] in Lg3 linkage group located a LOD value for quantitative trait loci (QTL) 2. 28, explaining the 16. 8% of the phenotypic differences; Ogundiwin [J] to find the five anti disease gene related QTLs: Phyto-Q, Phyto-R, Phyto-S, Phyto-T and Phyto-U. Their research results not the same, and other research results are not the same. In this study, the N3 linkage group, 1 QTL, located between EST451 to EST191, can explain the phenotypic variation of the disease resistant to 14.9%, and the results of previous studies are not the same. In summary, different researchers have obtained different results, analysis of the reasons may be due to the different various researchers use the mapping population, inoculation of Phytophthora species and resistance identification method, coupled with the pepper genome itself is relatively large, the genetic mechanisms of resistance to more complex, increased the difficulty of molecular markers, making each of the results is difficult to achieve. Therefore, it is necessary to study the resistance breeding of pepper.
Reference
[1] Wang Zhongwu, Ban Dequan. Comparison of control effects of 6 Fungicides against Pepper Blight [J]. Jiangsu agricultural science, 2013,41 (6): 110-111.
[2] THABUIS A,PALIOIX A,SERVIN B,et al. Marker-assisted in-trogression of Phytophthora apsici resistance QTL alleles into a bellpepper line: Validation of additive and epistatic effects [J]. Mo-lecular Breeding,2004,14 ( 1) : 9-20.
[3] TANKSLEY S D. Linkage relationships and chromosomal locationsof enzyme-coding genes in pepper,Capsicum annuum [J]. Chro-mosoma,1984,89 ( 5) : 352-360.
[4] MIMURA Y,INOUE T,KUBO N,et al. A SSR-based geneticmap of pepper ( Capsicum annuum L. ) servers as an anchor forthe alignment of major of pepper maps[J]. Breed Sci,2012,62:93-98.
[5] THABUIS A,PALLOIX A,PFIEGER S,et al. Comparative map-ping ofPhytophthora resistance loci in pepper germplasm: evidencefor conserved resistance loci across Solanceae and for a large geneticdiversity [J]. Theor Appl Genet,2003,106: 1473-1485.
[6] QUIRIN E A,OGUNDIWIN E A,PRINCE J P,et al. Develop-ment of sequence characterized amplified region ( SCAR) primersfor the detection of Phyto. 5. 2,a major QTL for resistance to Phy-tophthora capsici Leon in pepper [J]. Theoretical and Applied Ge-netics,2005,110: 605-612.